Installing Solace Schema Registry with Helm
This section provides detailed instructions for installing Solace Schema Registry on a Kubernetes cluster using Helm. It covers prerequisites, deployment architecture, and step-by-step installation procedures.
Prerequisites
Before deploying Solace Schema Registry, ensure you have:
- A Kubernetes cluster, version 1.21+ (1.19+ minimum supported).
- Helm 3.8+ installed (3.0+ minimum supported).
kubectlconfigured to communicate with your cluster.- Access to Solace Schema Registry container images from the Solace Products website. An account is required to access these images.
Minimum System Requirements for Production
The following are the minimum CPU, memory and storage resources required to run Solace Schema Registry in a production environment:
| Component | CPU (per pod) | Memory (per pod) | Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Database Pods | 500m request/limit | 256Mi request/limit |
|
| UI, IDP, and Backend Pods | 1000m request/limit | 256Mi request/limit |
|
values.yaml file. For production deployments, ensure you allocate sufficient resources based on your expected workload and high availability requirements.Multi-Node Cluster Requirements
For high availability deployments, Solace Schema Registry requires a minimum of three nodes in your Kubernetes cluster. This ensures proper distribution of services and database replicas across multiple nodes for fault tolerance.
Deployment Architecture
The Solace Schema Registry deployment on Kubernetes consists of the following components:
- schema-registry-backend—Handles API requests and schema management.
- schema-registry-ui—Provides the web interface for schema management.
- schema-registry-db-cluster—Database that stores schema definitions and metadata.
- schema-registry-idp—Identity provider that manages authentication and authorization.
The diagram below illustrates the Kubernetes deployment architecture of Solace Schema Registry:
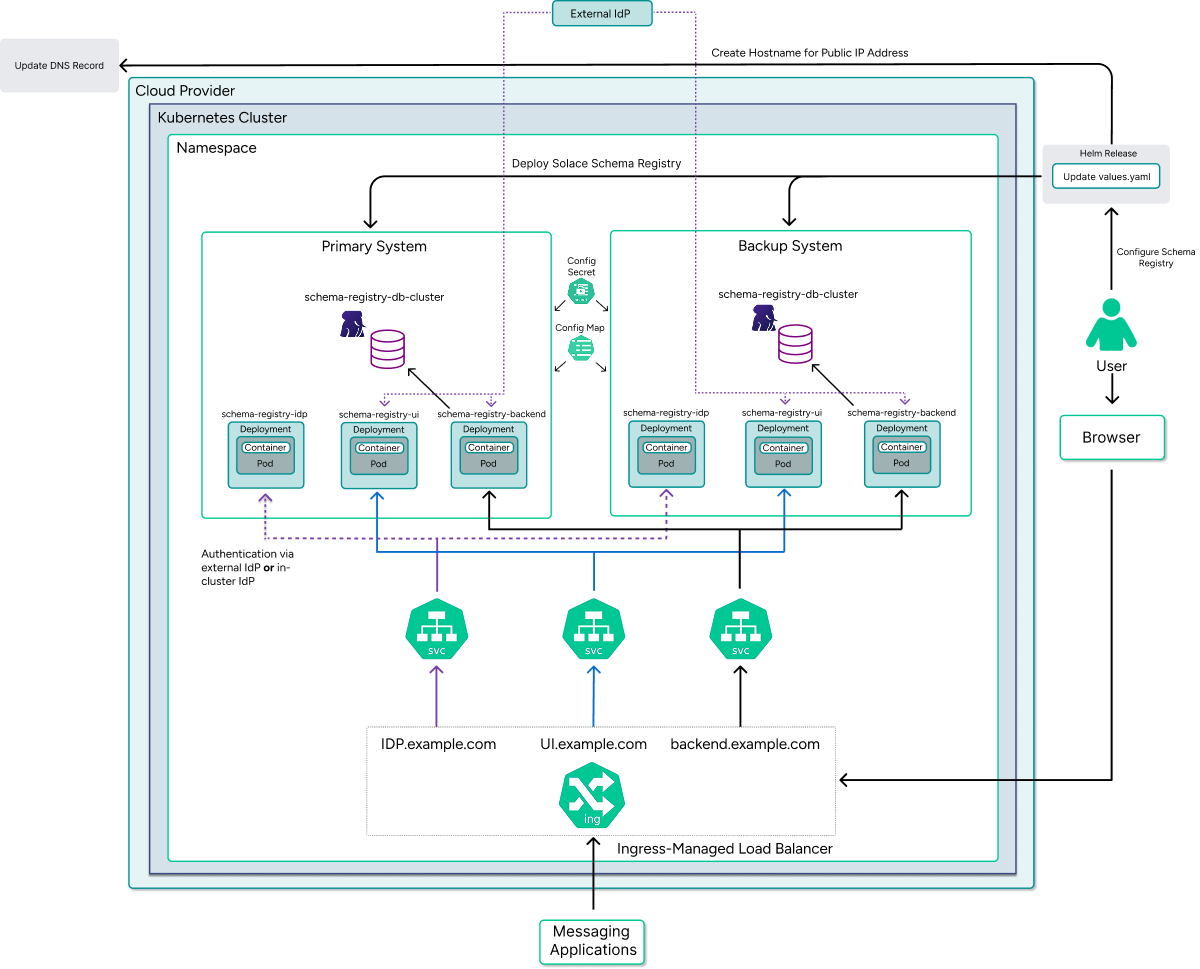
Key aspects of this architecture include:
- Backend System—A Kubernetes Deployment with multiple replicas for high availability. It connects to both the database for schema storage and the IdP for authentication. The Backend Service is exposed externally through an Ingress controller with path-based routing (typically at
/apis/registry/v3). - Database—PostgreSQL is deployed by the Helm chart using the CloudNative PostgreSQL Operator. This provides:
- Persistent storage through Kubernetes
PersistentVolumeClaims - High availability with one read-write primary and multiple read-only replicas
- Automatic failover managed by the operator
The database deployment requires a properly configured StorageClass in your Kubernetes cluster. After deployment, you are responsible for database management tasks (upgrades, backups, etc.) through the CloudNative PostgreSQL Operator.
- Persistent storage through Kubernetes
- External Identity Provider (IdP)—Connection to an existing external IdP, for example Microsoft Entra ID or Okta.
- Internal Identity Provider (IdP)—A built-in IdP service deployed as part of the Helm chart for development and testing purposes. Provides pre-configured users (sr-developer, sr-readonly) with customizable passwords for quick setup without requiring external authentication infrastructure.
For HA deployments, each site contains almost identical stacks with the main difference being the PostgreSQL configuration. The Solace Schema Registry itself runs in an active-active configuration, while the database operates in an active-standby mode with the Kubernetes operator handling failover in case of site failure.
Installation Steps
Follow these steps to install Solace Schema Registry using Helm:
- Retrieve Solace Schema Registry from the Solace Products website and extract the package:
tar -xzf schema-registry-v1.0.0.tar.gz && cd schema-registry-v1.0.0
- Load the Solace Schema Registry Docker images into your container registry. The images are provided as part of the distribution package.
Linux/Mac:
export REGISTRY="your-registry.com/project" for img in docker-images/*.tar.gz; do LOADED=$(docker load -i "$img" | grep "Loaded image:" | cut -d' ' -f3) NEW_NAME="$REGISTRY/$(basename "$img" .tar.gz)" docker tag "$LOADED" "$NEW_NAME" docker push "$NEW_NAME" done
Windows (CMD):
set REGISTRY=your-registry.com/project for %i in (docker-images\*.tar.gz) do ( for /f "tokens=3" %j in ('docker load -i "%i" ^| findstr "Loaded image:"') do ( set LOADED=%j for %k in ("%i") do set BASENAME=%~nk docker tag %LOADED% %REGISTRY%/%BASENAME% docker push %REGISTRY%/%BASENAME% ) ) - Install the CloudNative PostgreSQL Operator for database management:
kubectl apply --server-side -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloudnative-pg/cloudnative-pg/release-1.26/releases/cnpg-1.26.0.yaml
- (Optional) Install an ingress controller to access Solace Schema Registry services from outside the cluster. The Helm chart supports any Kubernetes-compatible ingress controller.
If you already have an ingress controller, you can skip the installation commands below and configure your
values.yamlto use your existing controller by specifying the ingress class in the annotations:ingress: annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "your-existing-ingress-class"If you need to install an ingress controller, example using NGINX:
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx helm repo update helm install nginx-ingress ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx \ --namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace
Alternative Ingress Controllers:
- Traefik
- HAProxy
- Kong
- Cloud provider ingress (AWS ALB, GCP Load Balancer, Azure Application Gateway)
Verify the ingress controller is running before proceeding:
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
- Configure TLS certificates. TLS configuration is required as Solace Schema Registry is not accessible over plain HTTP. You can configure certificates using your preferred method:
- cert-manager—For automated certificate management with Let's Encrypt or other ACME providers
- Commercial CA—Certificates from a trusted certificate authority
- Cloud provider services—AWS Certificate Manager, Google-managed certificates, Azure Key Vault
Ensure
ingress.tls.enabled: trueis set in yourvalues.yamlfile and provide the certificate and key in theingress.tls.crtandingress.tls.keyfields. For detailed TLS configuration options, see Ingress and TLS Configuration. - Navigate to the
helm-chartsdirectory and update thevalues.yamlfile with your environment-specific configuration. For detailed configuration options, see Configuring the Helm Chart. - Install Solace Schema Registry using Helm:
helm upgrade --install schema-registry ./solace-schema-registry
- Verify the deployment:
kubectl get pods -n solace
You should see pods for the backend service, UI service, database, and identity provider all in the
Runningstate. This might take a couple of minutes. - Access the deployed services. Replace
<ingress.hostNameSuffix>with the actual hostname or IP address you configured for your ingress:- UI Service:
https://ui.<ingress.hostNameSuffix>
When using the internal Identity Provider, log in with one of the following credentials:
sr-developer:<devPassword>—For developer role accesssr-readonly:<roPassword>—For read-only access
Replace
<devPassword>and<roPassword>with the values you set in theidp.developerPasswordandidp.readonlyPasswordfields in yourvalues.yamlfile. For more information, see Authentication and Security. - UI Service:
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
If you encounter issues during installation, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Images not loaded:
- Verify images are in your registry:
docker images | grep solace - Check the
dockerconfigjsonvalue in yourvalues.yamlis correctly base64-encoded - Ensure the
imagePullPolicyis set appropriately (typicallyIfNotPresentfor local registries)
- Verify images are in your registry:
- Pod startup failures:
- Check pod logs:
kubectl logs -n solace <pod-name> - Check for failure events:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n solace - Verify environment variables are correctly set
- Check for resource constraints (CPU, memory) that might prevent pods from starting
- Check pod logs:
- CloudNative PostgreSQL Operator issues:
- Verify the operator is running:
kubectl get pods -n cnpg-system - Check operator logs:
kubectl logs -n cnpg-system <operator-pod-name>
- Verify the operator is running:
- Database connection issues:
- Verify database credentials in your
values.yaml - Check database service is running:
kubectl get svc -n solace - Ensure network policies allow communication between Solace Schema Registry and database pods
- Verify database credentials in your
Enhanced Deployment Verification
Use the following commands to verify your deployment status:
kubectl get pods -n solace kubectl get svc -n solace kubectl get ingress -n solace
Check service health:
- UI Healthcheck:
curl -k https://ui.<your-domain>/ui/healthcheck - Backend Healthcheck:
curl -k https://apis.<your-domain>/apis/registry/v3 - IDP OIDC Configuration:
curl -k https://idp.<your-domain>/.well-known/openid-configuration