Creating an Event Mesh
You can use Broker Manager to set up an event mesh using Dynamic Message Routing (DMR). Before you configure your event mesh, ensure that you understand the DMR core concepts described in DMR Terminology and Best Practices for Designing an Event Mesh with DMR. For information about setting up an event mesh using the Solace Event Broker CLI, see Setting up an Event Mesh Using DMR.
To set up an event mesh using DMR, you need to establish:
- One or more clusters.
- Two or more DMR nodes (a software event broker or a high availability (HA) group).
- One or more DMR links between nodes.
With DMR, event brokers dynamically discover how to route messages. Client applications don't have to take any special action to publish or consume messages across the event mesh.
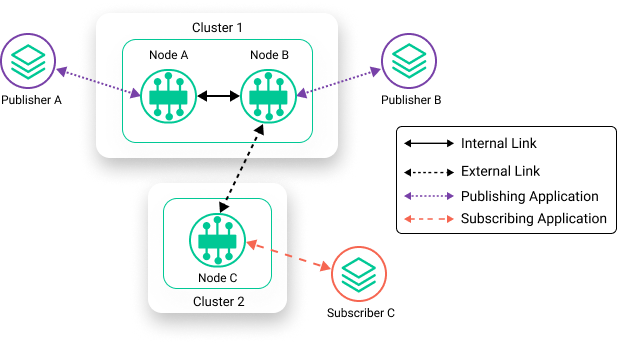
Consider this example where Subscriber C is connected to Node C, but is interested in events from Publisher A and Publisher B. In this scenario, none of the nodes can share information. The events from the publishers never arrive to the subscribers. For a subscribing application to receive topics from a publisher, it must be connected to the same event broker.
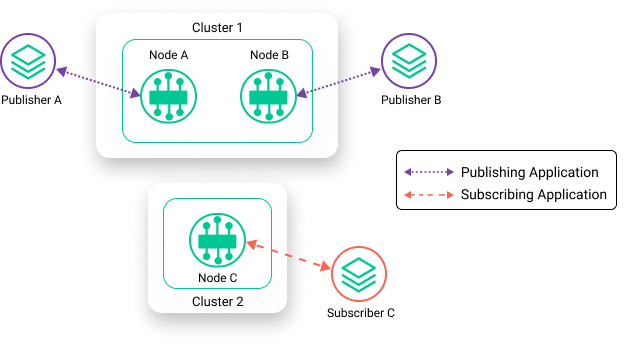
In comparison, the diagram below shows the event brokers configured as an event mesh. Subscribed events from both Publisher A and Publisher B are shared with Node A and Node B and can then be received by Subscriber C. As a result, Subscriber C can connect to one node in Cluster 1, and receive all subscribed events from the publishing applications that are connected to any node in the event mesh.
This topic includes the following tasks:
Creating a Cluster
To create a cluster using Broker Manager, perform these steps:
- Open Broker Manager. For instructions, see Broker Manager.
- On the navigation bar, select Clustering.
- Click Create a New Cluster.
- Enter a name and a password for the cluster.
- (Optional) Edit the following settings as required for the cluster:
Setting Description Basic Authentication Specifies whether the cluster uses basic authentication Type
Specifies the type of basic authentication the cluster will use for DMR links. - Internal Database—The cluster uses the locally configured password.
- None—The cluster doesn't use authentication.
Client Certificate Authentication Specifies whether client certificate authentication is used for cluster links. Content Specifies the PEM formatted content for the client certificate used to login to the remote node. It must consist of a private key and between one and three certificates comprising the certificate trust chain. Validate Server Name
Specifies whether the TLS authentication mechanism of verifying the name is used to connect to the bridge. If enabled, the name used to connect to the bridge is checked against the names specified in the certificate returned by the remote broker.
Maximum Chain Depth Specifies the maximum the number of signing CA certificates that are present in the chain back to a trusted self-signed root CA certificate. Validate Certificate Dates Specifies whether certificate "Not Before" and "Not After" validity dates are used. Direct Messaging Only Specifies whether the cluster uses direct messaging. - Click Apply.
- You may get a warning about the spool size being too small. Unless you are moving large amounts of data between brokers, you can click Continue to bypass the warning with no repercussions. For information about changing the maximum amount of spool usage, see Configuring Max Spool Usage.
You have now created a cluster for your event broker. You can see your cluster in the Summary tab. If you want to add more nodes to the cluster, see Adding a Node to a Cluster.
Configuring DMR Links
A cluster link connects nodes within a cluster or between two different clusters and allows them to exchange topology information, subscriptions, and data. A cluster link is composed of a control channel, a client profile, and one data channel per Message VPN.
External Links
Links between nodes that belong to different clusters are called external links. External links have a DMR bridge, which connects gateway nodes and allows messages published in one cluster to be delivered to the consumers of another cluster. Only clusters that are directly connected via an external link can exchange messages.
You can use Broker Manager to configure DMR external links for your event mesh.
For more information, see Configuring DMR External Links.
Internal Links
Links between nodes that belong to the same cluster are called internal links. Internal links allow messages published in one node to be delivered to consumers connected to another node. For subscriptions to be shared between every node in a cluster, internal links must be configured between every pair of nodes.
You can use Broker Manager to configure DMR internal links for your event mesh.
For more information, see Configuring DMR Internal Links.
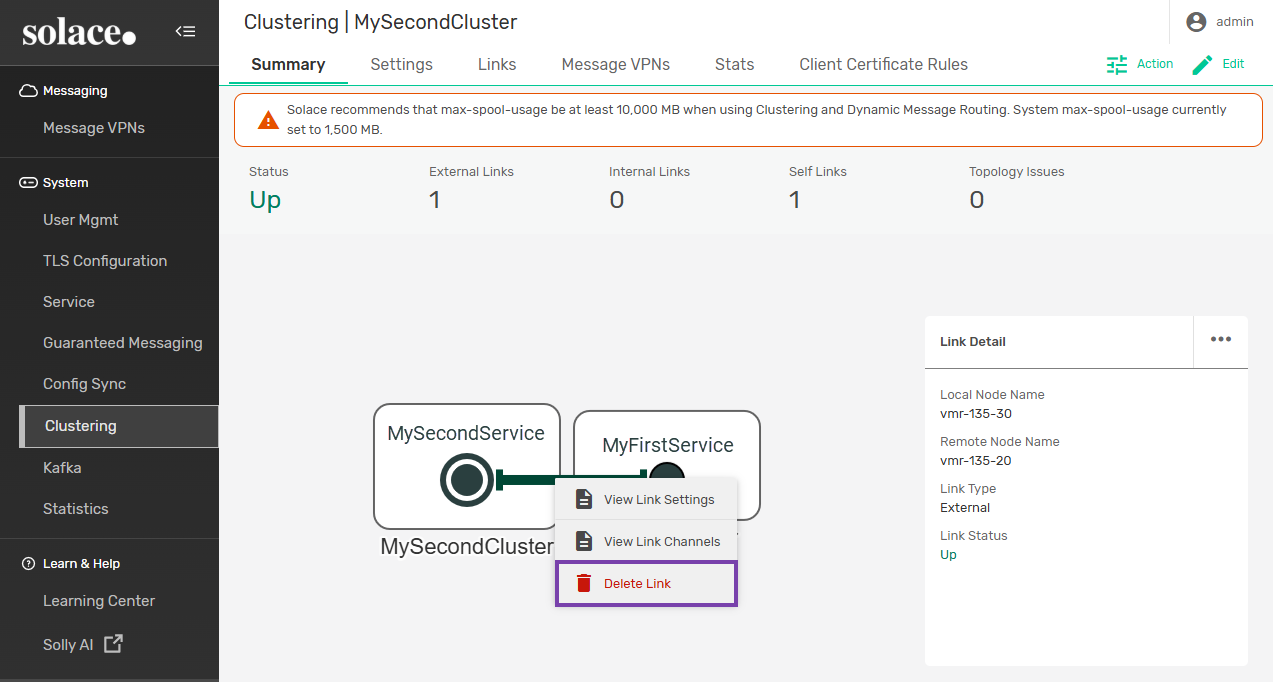
Deleting Links Between Nodes
Deleting a link from a node removes the connection from one side of the DMR link. If the link is deleted from only one node, it remains on the other node and may cause topology issues or prevent new links from being configured between the nodes.
To remove a link between two nodes, perform these steps:
- If you haven't already, open Broker Manager for the event broker that you used to configure one of the clusters you want to unlink. For instructions, see Broker Manager.
- On the navigation bar, select Clustering.
- Right click the link you want to remove. Select Delete Link and then click OK.
- Navigate to Broker Manager for the event broker that you used to configure the other cluster you want to unlink.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 to delete the link.
- If you do not delete the link from both nodes, the link will still be enabled and viewable on the summary page for one node, but it will not be operational.