Acknowledging Messages Received by Clients in the Solace JCSMP API
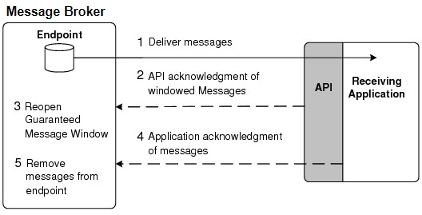
The Solace JCSMP API provides acknowledgments to the Solace event broker for the Guaranteed messages that clients receive through a Flow. The figure below shows the process of how the guaranteed messages that an application receives through a Flow are acknowledged. During this Flow, client applications can also send a negative acknowledgment (NACK) for malformed messages or messages that could not be processed.
Acknowledging Received Guaranteed Messages
API Acknowledgments
A Guaranteed message window size limits the number of messages that the API can receive before it must return an acknowledgment to the event broker to indicate that it received the messages in the window. After the API sends this acknowledgment, the Guaranteed message window reopens so that further messages can be sent to the API.
An application can adjust the windowed acknowledgments by changing the default acknowledgment timer and threshold parameters set through the Flow properties (refer to Important Flow (Message Consumer) Properties). Changing these defaults is not usually required and will change the performance characteristics of a Flow.
Application Acknowledgments
One of the two following application acknowledgment modes can be used for acknowledging a message:
- Auto-acknowledgment
- Client acknowledgment
The acknowledgment mode to use is set through one of the flow properties listed below. By default, the auto-acknowledgment mode is used.
The following code shows how to perform acknowledgment for the different APIs:
ConsumerFlowProperties.setAckMode(String ackMode)
Possible values for ackMode are:
-
JCSMPProperties.SUPPORTED_MESSAGE_ACK_AUTO -
JCSMPProperties.SUPPORTED_MESSAGE_ACK_CLIENT
Auto-Acknowledgment Mode
When the auto-acknowledgment mode is used, the API automatically generates application-level acknowledgments.
For JCSMP, acknowledgments are sent at different times depending on whether the message is received asynchronously or synchronously:
- when received asynchronously, the acknowledgment is sent after the message callback completes.
- when received synchronously, the acknowledgment is sent after the message is removed from the API's internal queue during the
receive()method. It's important to realize that the acknowledgment has been sent before control is returned to the application (that is after thereceive()method completes).
Client Acknowledgment Mode
When the client acknowledgment mode is used the client must explicitly send an acknowledgment for the message ID of each message received. Optionally, you can use negative acknowledgments as well. For more information, see Negative Acknowledgments for Specific Messages.
To explicitly send a client acknowledgment, use XMLMessage.ackMessage().
Avoid allowing the number of outstanding unacknowledged messages to become excessively large (for example, 10,000 or more) because the egress message rate from the event broker can start to decline.
Negative Acknowledgments for Specific Messages
You can use negative acknowledgments (NACKs) if you have configured your applications for client acknowledgments (see Client Acknowledgment Mode). When you use NACKs, you can send a settlement outcome to let the event broker know the result from processing a guaranteed message that was received. Based on the settlement outcome, the event broker knows how to handle the message on its queue. You can use the following settlement outcomes:
- ACCEPTED—This ACK notifies the event broker that your client application successfully processed the guaranteed message. When the event broker receives this outcome it removes the message from its queue.
- When you call a settlement function/methods with an outcome of ACCEPTED, it is the same as calling an ACK function/methods in Client Acknowledgment Mode.
- FAILED—This NACK notifies the event broker that your client application did not process the message. When the event broker receives this NACK it attempts to redeliver the message while adhering to delivery count limits.
- REJECTED—This NACK notifies the event broker that your client application could process the message but it was not accepted (for example, failed validation). When the event broker receives this NACK it removes the message from its queue and then moves the message to the Dead Message Queue (DMQ) if it is configured.
Before you can use NACK s, you must add the FAILED, REJECTED, or both outcomes as NACK types when you create the Flow to prepare the Flow to work with negative acknowledgments. You do not need to add the ACCEPTED outcome because it is always available. If you try to use an outcome that has not been added, you get an error of Required Settlement Outcome Not Supported.
- NACKs can be lost during transit (for example due to unexpected networking issues). Consider this fact as part of the logic for handling messages when you develop your application.
- NACKs are supported on event brokers 10.2.1 and later. If an event broker does not support NACKs, an
InvalidOperationExceptionoccurs during the Flow bind request when an outcome is specified.
Using NACKs with the Solace JCSMP API
To use NACKs with the Solace JCSMP API, do the following:
- Enable and prepare the Flow to use negative acknowledgments:
ConsumerFlowProperties.addRequiredSettlementOutcomes(Outcome outcometoadd) - You need to add one or both of:
Outcome.FAILEDOutcome.REJECTEDOutcome.ACCEPTEDis not required to be set and always supported.
- You can ACK or NACK using:
XMLMessage.settle(settlement_outcome) - Possible values to use:
Outcome.ACCEPTEDOutcome.FAILEDOutcome.REJECTED
The following sample code shows how to send NACKs:
// A session has already been created with JCSMPProperties.SUPPORTED_MESSAGE_ACK_CLIENT
final ConsumerFlowProperties cfp = new ConsumerFlowProperties().setEndpoint(q);
// Add the settlement outcomes - Outcome.ACCEPTED does not need to be added because it is always included
// The consumer can add multiple outcomes, for example cfp.addRequiredSettlementOutcomes(Outcome.FAILED, Outcome.REJECTED);
cfp.addRequiredSettlementOutcomes(Outcome.FAILED);
final FlowReceiver flowReceiver= session.createFlow(null, cfp);
BytesXMLMessage msg = flowReceiver.receive(1000);
try {
processMessage(msg);
msg.settle(Outcome.ACCEPTED);// same as msg.ackMessage();
catch (Exception e){
msg.settle(Outcome.FAILED); // Failed to process message, settle as FAILED
}
}
For more information, see the Solace Messaging API for JCSMP reference.